General Alexander S. Webb
"General Webb, born in New York city, February 15th, 1835, was graduated from the United States Military…

Frederick City
"General McClellan and the Federal troops passing through Frederick City, Md., in pursuit of the Confederate…

Cavalry of General Banks
"A reconnoitring detachment of General Banks's cavalry, Hyattstown, Md., in the distance. There are…

Conrad's Ferry
"Conrad's Ferry, Md., above Harrison's Island, on the Potomac River, the place of passage of Colonel…

Oven
"'Fresh Bread!'- Impromptu oven built by the Nineteenth Regiment, New York Volunteers, in General Banks's…

General Burnside
"Major General Burnside assuming command of the Army of the Potomac- issuing orders to his staff. 'Headquarters,…

Battle of Antietam
"Battle of Antietam, Md. Burnside's division carrying the bridge over the Antietam Creek and storming…

Army of the Potomac
"Advance of the Army of the Potomac. Occupation of Winchester, VA., and the abandoned Confederate Fortifications,…

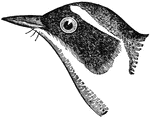
Common Seal
"The ground-color of the hair or skin, when this animal is alive and dry, is pale whitish-gray, with…

Hooded Seal
"Also called the Crested Seal, remarkable for possessing, about two inches from te extremity of the…

Sea Bear
"It is the size of a large bear; girth at the sholder, five feet, near the tail, twenty inches; fur…

Battle of Blue Ridge Pass
"Battle of Blue Ridge Pass, Sunday, September 14th, 1862- the first Federal victory in Maryland. On…

Confederate Invasion
"The Confederate invasion of Maryland and Pennsylvania. The Confederate cavalry crossing the Potomac,…

Loudon Heights
"View from Loudon Heights, Va., showing Harper's Ferry, Maryland Heights, Bolivar, etc. Harper's Ferry,…

Invasion of Maryland
"The invasion of Maryland- General Kilpatrick repulsing the Confederate Stuart at Boonsborough, July…

Falling Waters
"Gallant charge of the Sixth Michigan cavalry over the enemy's breastworks, near falling Waters, Md.,…

Lee's Army
"Lee's army crossing the Potomac at Williamsport, in scows guided by wires, after the invasion of Maryland."—…

Signal Station
"Federal signal station on Loudoun Heights, Harper's Ferry, communicating with the station on Maryland…

Daughters of Maryland
"How the Daughters of Maryland received the Sons of the North as they marched against the Confederate…

Invasion of Maryland
"The invasion of Maryland- citizens of Baltimore barricading the streets, Monday evening, June 29th,…

Antietam
"The invasion of Maryland--General Meade's Army crossing the Antietam in pursuit of Lee, July 12th,…

Farmers Visiting
"Maryland and Pennsylvania farmers visiting the battlefield of Antietam, while the Federal troops were…

Funeral Cortege
"The funeral cortege, at boston, Mass., of the Sixth Massachusetts soldiers killed at Baltimore. The…

Camp Ground
"View of the Camp Ground. This is from a painting by Tice, in my possession. The land on which the encampment…

Violet-colored salamander
"Is five to seven inches long,; blueish-black, with bright yellow spots; habits nocturnal, living under…
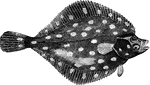
Plaice
"Weighing six to twelve pounds; it feeds on mollusca, crustacea, and young fish; inhabits sandy banks…

Penn's seal and signature
"Penn's Seal and Signature. This is a representation of the seal and signature of William Penn attached…

Washington Monument
"Washington Monument. The following are the inscriptions on the monument: East front: 'To George Washington,…

General Burnside
"Major General Burnside assuming command of the Army of the Potomac- issuing orders to his staff. 'Headquarters,…

William Tryon Seal
"Seal and signature of Tryon. William Tryon was a native of Ireland, and was educated to the profession…

William the Conqueror
"William the Conqueror (1066-1087), as represented on his seal. Although William really ruled 'as king…

John Brown
In 1859, John Brown collected a small body of men, white and black, in the mountains of Maryland. He…

Eagle on Seal of United States
"The Eagle is a gold coin of the United States, value $10; half-eagle, $5; quarter-eagle, $2.50, double…

Hooded Seal
"The Seal, of the family Phocidæ, or seal tribe, are, of all four-limbed mammiferous animals,…
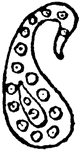
Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…

Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…
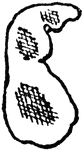
Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…

Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…
Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…
Pear Design
"Also known as the cone, the palm leaf, the river loop, the crown jewel, the seal, the almond, the feather,…
Solomon's Seal
Built on the right angle triangle and, like the Signet of David, it is found in many of the Turkish…

Elwell Otis
A soldier born in Frederick City, Maryland, March 25, 1838. After graduating at Rochester University,…